Despite the progresses carried out in the subject of radiotherapy, toxicity to the wholesome tissues stays a significant limiting issue. The intention of this work was to spotlight blood biomarkers whose variations may predict the incidence of late cutaneous unintended effects. Two teams of 9 sufferers handled for Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) had been established in accordance to the grade of late pores and skin toxicity after adjuvant irradiation for MCC: grade 0, 1 or 2 and grade Three or 4 of RTOG (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group)/EORTC (European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer).
To strive to discriminate these 2 teams, biomarkers of curiosity had been measured on the completely different blood compartments after ex vivo irradiation. In lymphocytes, cell cycle, apoptosis and genotoxicity had been studied.
Oxidative stress was evaluated by the willpower of the erythrocyte antioxidant capability (superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, decreased and oxidized glutathione) in addition to degradation merchandise (protein carbonylation, lipid peroxidation). Inflammation was assessed in the plasma by the measurement of 14 cytokines.
The most radiosensitive sufferers offered a lower in apoptosis, micronucleus frequency, antioxidant enzyme actions, glutathione and carbonyls; and a rise in TNF-a (Tumor Necrosis Factor a), IL-8 (Interleukin 8) and TGF-β1 (Transforming Growth Factor β1) ranges. These findings have to be confirmed on the next quantity of sufferers and earlier than radiotherapy and may enable to predict the incidence of late pores and skin unintended effects after radiotherapy.
Only susceptible adults present change in continual low-grade irritation after contemplative psychological coaching: proof from a randomized scientific trial
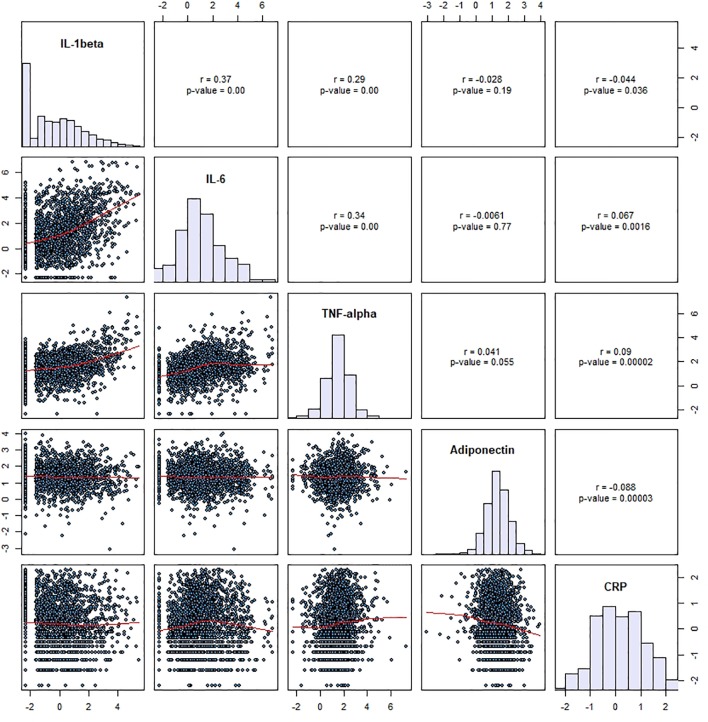
Growing proof means that continual low-grade irritation will be decreased by means of mindfulness-based psychological coaching interventions. However, these outcomes are inconsistent and primarily based on affected person populations with heterogeneous circumstances. Similar analysis in wholesome adults is missing.
Moreover, widespread intervention protocols contain various mixtures of completely different contemplative practices, such that it stays unclear which varieties of coaching most successfully affect biomarkers of irritation. The current research investigated the impact of three distinct 3-month coaching modules cultivating a) interoception and present-moment focus (Presence), b) socio-affective abilities (Affect), or c) socio-cognitive abilities (Perspective) on the inflammatory biomarkers interleukin-6 (IL-6) and excessive delicate C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) in 298 wholesome adults.
We noticed no group-level impact of coaching on both biomarker, however trend-level interactions of coaching sort and participant intercourse. In moreover exploring the affect of contributors’ baseline irritation, a selective coaching impact emerged: Following the Presence module, contributors with comparatively greater inflammatory load confirmed stronger discount in IL-6 on common, and in hs-CRP in the event that they had been male.
Mindfulness- and attention-based psychological follow thus seems only when concentrating on continual low-grade irritation in wholesome adults, notably in males.
Overall, our knowledge level to a ground impact in the discount of inflammatory markers by means of contemplative psychological coaching, suggesting that psychological coaching could also be much less efficient in enhancing basal organic well being outcomes in wholesome, low-stressed adults than in susceptible populations.
Anti-IL-12/23p40 antibodies for upkeep of remission in Crohn’s illness
Ustekinumab and briakinumab are monoclonal antibodies that focus on the commonplace p40 subunit of cytokines interleukin-12 and interleukin-23 (IL-12/23p40), that are concerned in the pathogenesis of Crohn’s illness (CD).
A big proportion of folks with Crohn’s illness fail typical remedy or remedy with biologics (e.g. infliximab) or develop important opposed occasions. Anti-IL-12/23p40 antibodies corresponding to ustekinumab could also be an efficient various for these people.The goals of this evaluation had been to assess the efficacy and security of anti-IL-12/23p40 antibodies for upkeep of remission in CD.
We searched the Cochrane IBD Group Specialized Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, and trials registers from inception to 17 September 2019. We searched references and convention abstracts for extra research.We thought-about for inclusion randomized managed trials wherein monoclonal antibodies in opposition to IL-12/23p40 had been in contrast to placebo or one other lively comparator in contributors with quiescent CD.
Two evaluation authors independently screened research for inclusion, extracted knowledge, and assessed bias utilizing the Cochrane ‘Risk of bias’ device. The major end result measure was failure to keep scientific remission, outlined as a Crohn’s illness exercise index (CDAI) of < 150 factors. Secondary outcomes included failure to keep scientific response, opposed occasions (AE), critical opposed occasions (SAE), and withdrawals due to AEs. Clinical response was outlined as a lower in CDAI rating of ≥ 100 factors from baseline rating.
We calculated the threat ratio (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for every end result. We analyzed all knowledge on an intention-to-treat foundation. We used GRADE to consider the total certainty of the proof supporting the outcomes.Three randomized managed trials (646 contributors) met the inclusion standards.
Two trials assessed the efficacy of ustekinumab (542 contributors), and one research assessed the efficacy of briakinumab (104 contributors). We assessed all of the included research as at low threat of bias. One research (N = 145) in contrast subcutaneous ustekinumab (90 mg) administered at 8 and 16 weeks in contrast to placebo. Fifty-eight per cent (42/72) of ustekinumab contributors failed to keep scientific remission at 22 weeks in contrast to 73% (53/73) of placebo contributors (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.63 to 1.02; moderate-certainty proof).
Failure to keep scientific response at 22 weeks was seen in 31% (22/72) of ustekinumab contributors in contrast to 58% (42/73) of placebo contributors (RR 0.53, 95% CI 0.36 to 0.79; moderate-certainty proof). One research (N = 388) in contrast subcutaneous ustekinumab (90 mg) administered each Eight weeks or each 12 weeks to placebo for 44 weeks.
Forty-nine per cent (126/257) of ustekinumab contributors failed to keep scientific remission at 44 weeks in contrast to 64% (84/131) of placebo contributors (RR 0.76, 95% CI 0.64 to 0.91; moderate-certainty proof). Forty-one per cent (106/257) of ustekinumab contributors failed to keep scientific response at 44 weeks in contrast to 56% (73/131) of placebo contributors (RR 0.74, 95% CI 0.60 to 0.91;
moderate-certainty proof). Eighty per cent (267/335) of ustekinumab contributors had an AE in contrast to 84% (173/206) of placebo contributors (RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.87 to 1.03; high-certainty proof).
Commonly reported opposed occasions included infections, injection website reactions, CD occasion, stomach ache, nausea, arthralgia, and headache. Eleven per cent of ustekinumab contributors had an SAE in contrast to 16% (32/206) of placebo contributors (RR 0.74, 95% CI 0.48 to 1.15; moderate-certainty proof).
SAEs included critical infections, malignant neoplasm, and basal cell carcinoma. Seven per cent (5/73) of ustekinumab contributors withdrew from the research due to an AE in contrast to 1% (1/72) of placebo contributors (RR 4.93, 95% CI 0.59 to 41.18; low-certainty proof).
Worsening CD was the commonest motive for withdrawal due to an AE. One research in contrast intravenous briakinumab (200 mg, 400 mg, or 700 mg) administered at weeks 12, 16, and 20 with placebo. Failure to keep scientific remission at 24 weeks was seen in 51% (32/63) of briakinumab contributors in contrast to 61% (22/36) of placebo contributors (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.58 to 1.20; low-certainty proof). Failure to keep scientific response at 24 weeks was seen in 33% (21/63) of briakinumab contributors in contrast to 53% (19/36) of placebo contributors (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.40 to 1.02; low-certainty proof).
Sixty-six per cent (59/90) of briakinumab contributors had an AE in contrast to 64% (9/14) of placebo contributors (RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.67 to 1.55; low-certainty proof). Common AEs included higher respiratory tract an infection, nausea, stomach ache, headache, and injection website response.
Two per cent (2/90) of briakinumab contributors had an SAE in contrast to 7% (1/14) of placebo contributors (RR 0.31, 95% CI 0.03 to 3.21; low-certainty proof). SAEs included small bowel obstruction, deep vein thrombosis, and respiratory misery. Withdrawal due to an AE was famous in 2% of briakinumab contributors in contrast to 0% (0/14) of placebo contributors (RR 0.82, 95% CI 0.04 to 16.34; low-certainty proof). The AEs main to research withdrawal weren’t described.Moderate-certainty proof means that ustekinumab might be efficient for the upkeep of scientific remission and response in folks with reasonable to extreme CD in remission with out an elevated threat of opposed occasions (high-certainty proof) or critical opposed occasions (moderate-certainty proof) relative to placebo.
The impact of briakinumab on upkeep of scientific remission and response in folks with reasonable to extreme Crohn’s illness in remission was unsure as the certainty of the proof was low. The impact of briakinumab on opposed occasions and critical opposed occasions was additionally unsure due to low-certainty proof.
Further research are required to decide the long-term efficacy and security of subcutaneous ustekinumab upkeep remedy in Crohn’s illness and whether or not it must be utilized by itself or together with different brokers. Future analysis evaluating ustekinumab with different biologic drugs will assist to decide when therapy with ustekinumab in CD is most acceptable.
Currently, there may be an ongoing research that compares ustekinumab with adalimumab. This evaluation might be up to date when the outcomes of this research grow to be out there. The producers of briakinumab have stopped manufacturing of this medicine, thus additional research of briakinumab are unlikely.

