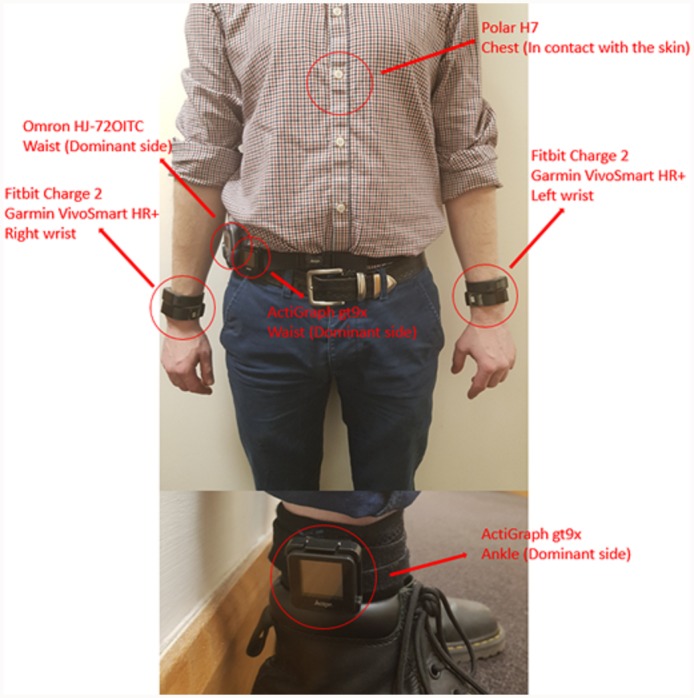
Wrist-worn activity trackers have skilled an amazing development these days and research on the accuracy of mainstream trackers utilized by older adults are wanted. This examine explores the efficiency of six trackers (Fitbit Charge2, Garmin VivoSmart HR+, Philips Health Watch, Withings Pulse Ox, ActiGraph GT9X-BT, Omron HJ-72OITC) for estimating: steps, travelled distance, and heart-rate measurements for a cohort of older adults. Eighteen older adults accomplished a structured protocol involving strolling duties, simulated family actions, and sedentary actions.
Less standardized actions had been additionally included, reminiscent of: dusting, utilizing a strolling support, or enjoying playing cards, in order to simulate real-life situations. Wrist-mounted and chest/waist-mounted units had been used. Gold-standards included treadmill, ECG-based chest strap, direct commentary or video recording in accordance with the activity and parameter. Every tracker confirmed a lowering accuracy with slower strolling velocity, which resulted in a major step under-counting.
A big imply absolute proportion error (MAPE) was discovered for each monitor at slower strolling speeds with the bottom reported MAPE at 2 km/h being 7.78%, growing to 20.88% at 1.5 km/h, and 44.53% at 1 km/h. During family actions, the MAPE climbing up/down-stairs ranged from 8.38-19.3% and 10.06-19.01% (dominant and non-dominant arm), respectively. Waist-worn units confirmed a extra uniform efficiency.
However, unstructured actions (e.g. dusting, enjoying playing cards), and utilizing a strolling support symbolize a problem for all wrist-worn trackers as evidenced by massive MAPE (> 57.66% for dusting, > 67.32% when utilizing a strolling support). Poor efficiency in travelled distance estimation was additionally evident throughout strolling at low speeds and climbing up/down-stairs (MAPE > 71.44% and > 48.3%, respectively). Regarding heart-rate measurement, there was no vital distinction (p-values > 0.05) in accuracy between trackers positioned on the dominant or non-dominant arm.
Concordant with current literature, whereas the imply error was restricted (between -3.57 bpm and 4.21 bpm), a single heart-rate measurement may very well be underestimated as much as 30 beats-per-minute. This examine confirmed a quantity of limitations of consumer-level wrist-based activity trackers for older adults. Therefore warning is required when used, in healthcare or in analysis settings, to measure activity in older adults.
A comparative analysis of sign high quality between a research-grade and a wi-fi dry-electrode cellular EEG system.
Electroencephalography (EEG) is extensively utilized by clinicians, scientists, engineers and different professionals worldwide, with an growing quantity of low-cost, commercially-oriented EEG techniques which have change into accessible in current years. One such system is the Cognionics Quick-20 (Cognionics Inc., San Diego, USA), which makes use of dry electrodes and gives the comfort of portability due to its built-in amplifier and wi-fi connection. Because of such traits, this method has been used in a number of functions for each scientific and fundamental analysis research.
However, an investigation of the standard of the indicators which might be recorded utilizing this method has not but been reported.To bridge this hole, right here we performed a scientific comparability of sign high quality between the Cognionics Quick-20 system and the Brain Products actiCAP/actiCHamp (Brain Products GmbH, Munich, Germany), a state-of-the-art, wet-electrode, research-oriented EEG system. Resting-state EEG information had been recorded from twelve human members at relaxation in eyes open and eyes closed circumstances.
For each techniques we evaluated the similarity of imply recorded energy spectral density, and detection of alpha suppression related to eyes open relative to eyes closed.Power spectral densities had been extremely correlated throughout techniques, with solely minor topographical variability throughout the scalp.
Both techniques recorded alpha suppression throughout eyes open relative to eyes closed circumstances.These outcomes attest to the robustness and reliability of the dry-electrode Cognionics system comparatively to the extensively used Brain Products laboratory EEG system, and thus validate its utility for scientific and fundamental analysis functions, at the very least in research in which members don’t transfer.

